Back from the ERC RESUS 2024 congress, Pierre Da Rocha, Clinical Specialist at Archeon Medical, shares some key takeaways from this event. Many presentations highlighted the crucial role of manual ventilation during CPR, a belief that has been advocated at Archeon Medical for several years.
Here are some key takeaways from the conference, including studies that utilized our EOlife device to collect critical data on manual ventilation quality.
Vecars 1
Study led by D. Jost, F. Lemoine, and the team at the Paris Fire Brigade
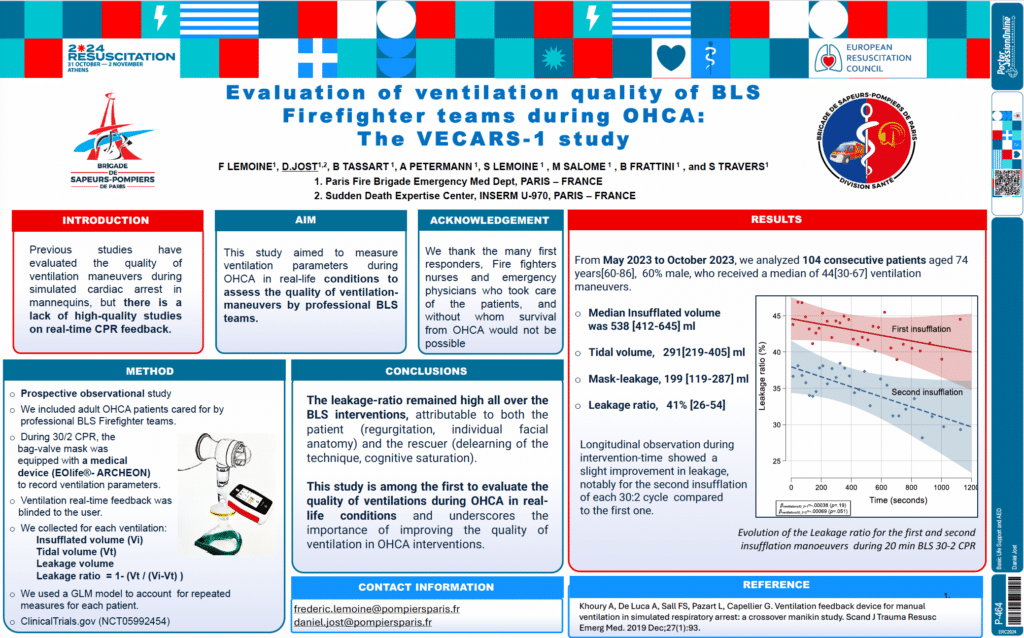
This study is the first to use EOlife in clinical conditions. The device was blinded and recorded the quality of manual ventilation provided by professional firefighters to OHCA patients. Results revealed a concerning deviation from ventilation guidelines, with an alarming 41% leakage ratio and a low average tidal volume of just 291mL.
Pediatric Ventilation Simulation Study
Study led by S. Lemoine and the Paris Fire Brigade team
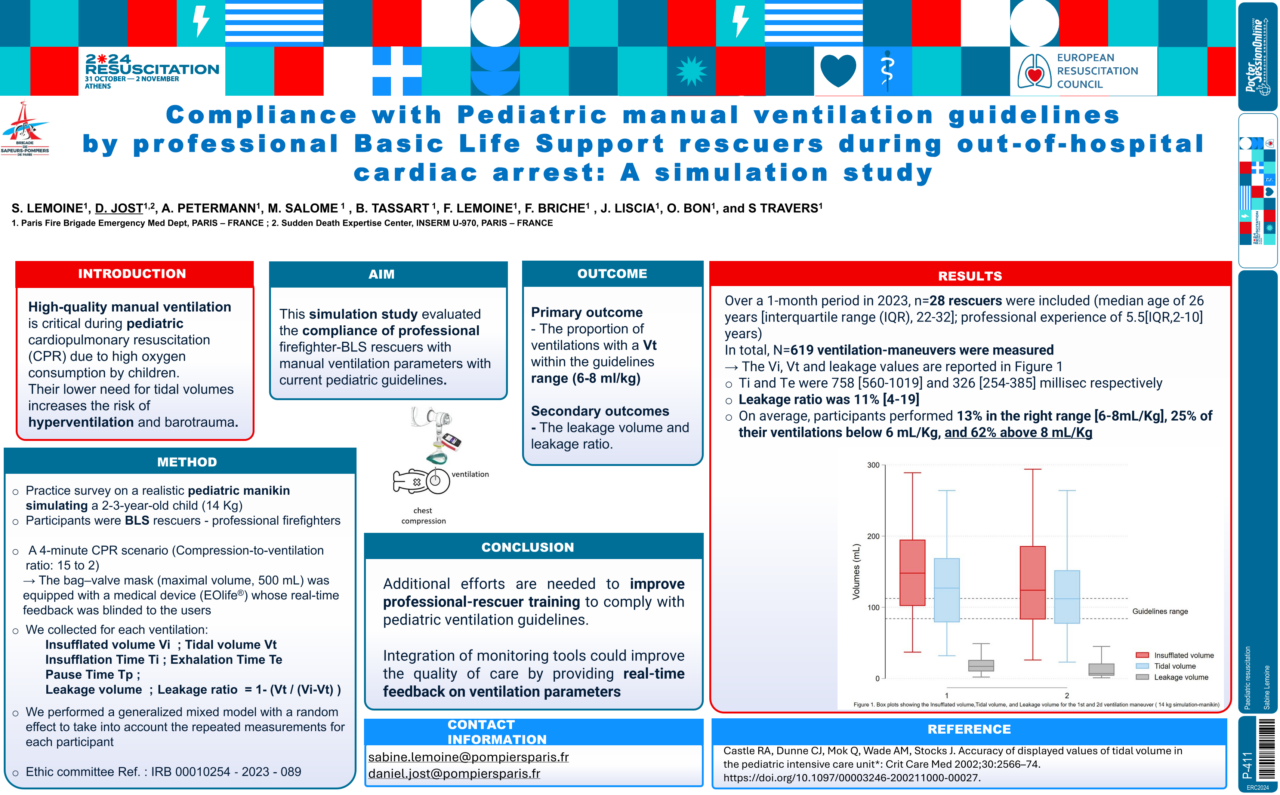
This simulation study evaluated 28 rescuers using EOlife with a blinded screen on a 2-3-year-old manikin. Only 13% of participants achieved the correct ventilation volume, while 62% hyperventilated, and 25% hypoventilated, highlighting the need for training and feedback in pediatric ventilation.
Manual Ventilation Quality Among Hospital Residents
Study led by the Santiago de Compostela University in Spain
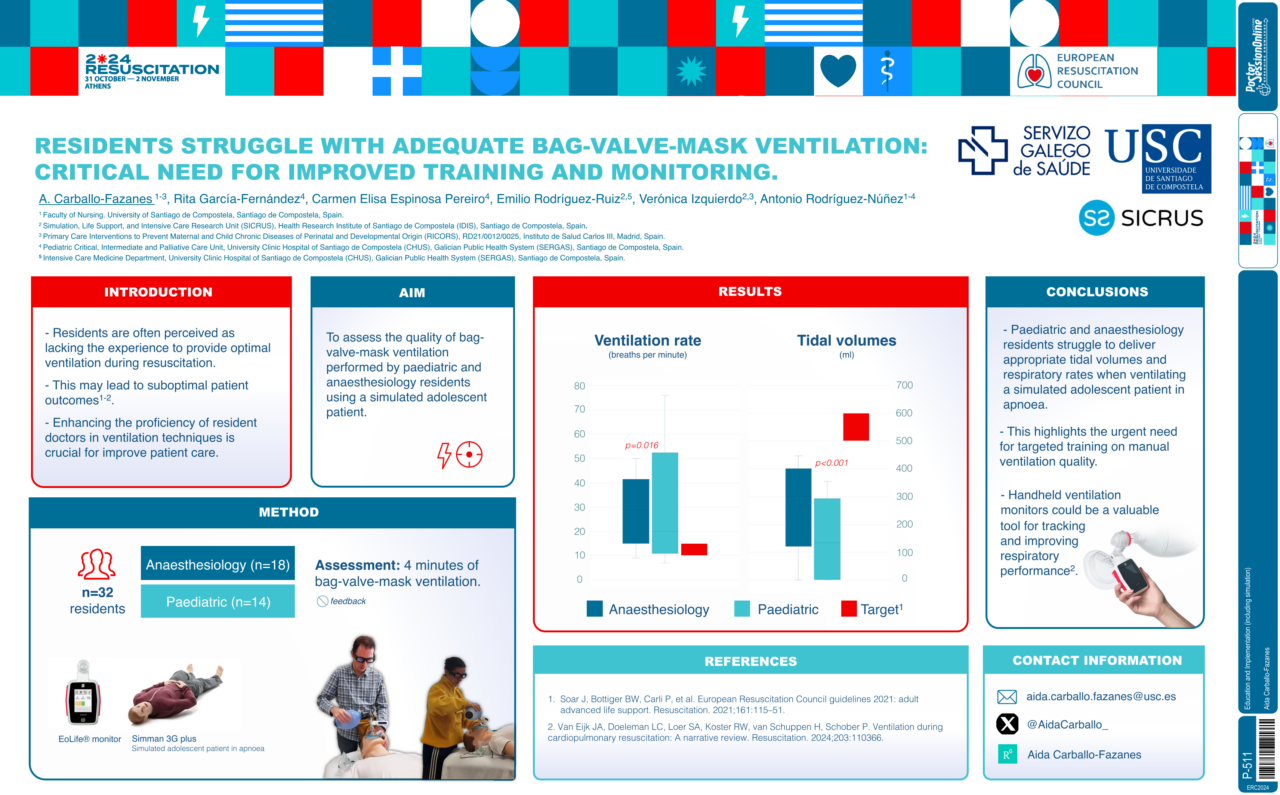
This study examined the ventilation quality provided by pediatric and anesthesiology residents on a simulated adolescent patient. Findings showed that residents struggled to deliver appropriate tidal volumes and respiratory rates, underscoring the importance of training and monitoring in clinical education.
On the final day of ERC RESUS, a significant conference session titled “Intra-Arrest Ventilation” was presented by S. Orlob, G. Debaty, J. Wittig, and K. Glerup Lauridsen. The speakers strongly emphasized the need for real-time manual ventilation feedback during CPR.
“Now we actually have several feedback devices on the market that can be used to assess both the rate and tidal volume. Really, it is the combined information on rate and tidal volume that gives us the ventilation. By measuring those simultaneously, we can at least get something that is a little bit qualified.”
K. Glerup Lauridsen
The ultimate medical device for high-performance manual ventilation.
Measure and adjust in real-time the quality of your manual ventilation. Medical device designed for the manual ventilation of adult patients in cardiopulmonary arrest.

The ultimate training tool for high-performance manual ventilation.
Record your training sessions. Analyze your ventilation cycles. Improve your manual ventilation practice.


